Prediction Markets: From Platforms to Protocols

Early prediction markets existed long before blockchains. They proved the core idea: markets can aggregate belief better than polls or pundits. But they were usually built as platforms, websites operated by a company, with rules enforced by databases and outcomes settled by administrators.
Even when the economics were sound, participants still depended on the operator to avoid midstream interference, resolve outcomes fairly, and honor payouts. That dependency wasn’t a footnote but a structural limit.
Blockchains changed that foundation. Prediction markets didn’t just move onto blockchains, they changed form. What used to be platforms became protocols.
So why does that change matter?
Code Over Counterparties
On a blockchain, the rules of a prediction market are written directly into smart contracts:
- How markets are created
- How trading works
- How prices move
- How outcomes settle
Once deployed, those rules execute automatically. Anyone can inspect them. No one can quietly modify them after the fact. Settlement doesn’t depend on an operator interpreting results or approving withdrawals. The system enforces itself.
This is not about eliminating trust entirely. It is about minimizing where trust is required. Instead of trusting a company, participants trust code whose behavior is public, deterministic, and constrained. Prediction markets stop being promises. They become machinery.
Permissionless Participation
When prediction markets live on public blockchains, access is no longer something that gets granted. There is no account approval, no jurisdictional whitelist, no central gatekeeper. Anyone can:
- Create a new market
- Trade existing outcomes
- Provide liquidity and earn fees
Markets emerge because someone cares enough to ask a question and others care enough to trade on it. The system doesn’t judge whether a question is important, appropriate, or popular. It simply provides the rails.
This permissionlessness has second-order effects. Niche questions become viable. Experimental formats appear. Market design itself becomes something people iterate on in public. The result is not a single “official” prediction market, but an ecosystem of them.
Markets as Infrastructure
The most important difference between on-chain prediction markets and earlier versions is not decentralization alone. It is composability. On-chain markets can plug directly into other on-chain systems:
- DeFi liquidity and collateral
- DAO treasuries and governance
- Insurance mechanisms
- Automated strategies
A prediction market no longer needs to be a destination you visit. It can be a component another system depends on. Its prices can be read, reacted to, and reused elsewhere. This is the moment prediction markets stop being applications and start becoming infrastructure.
On-Chain Market Stack
Once the idea clicks, the mechanics behind on-chain prediction markets are surprisingly well-structured. Most systems rely on the same key elements.
Market Contract & Outcome Tokens
Everything starts with a contract that defines the rules of the market. Prediction markets are unforgiving when it comes to ambiguity. A poorly phrased question can break incentives or lead to disputes. Clear wording is not a detail here but a must-have.
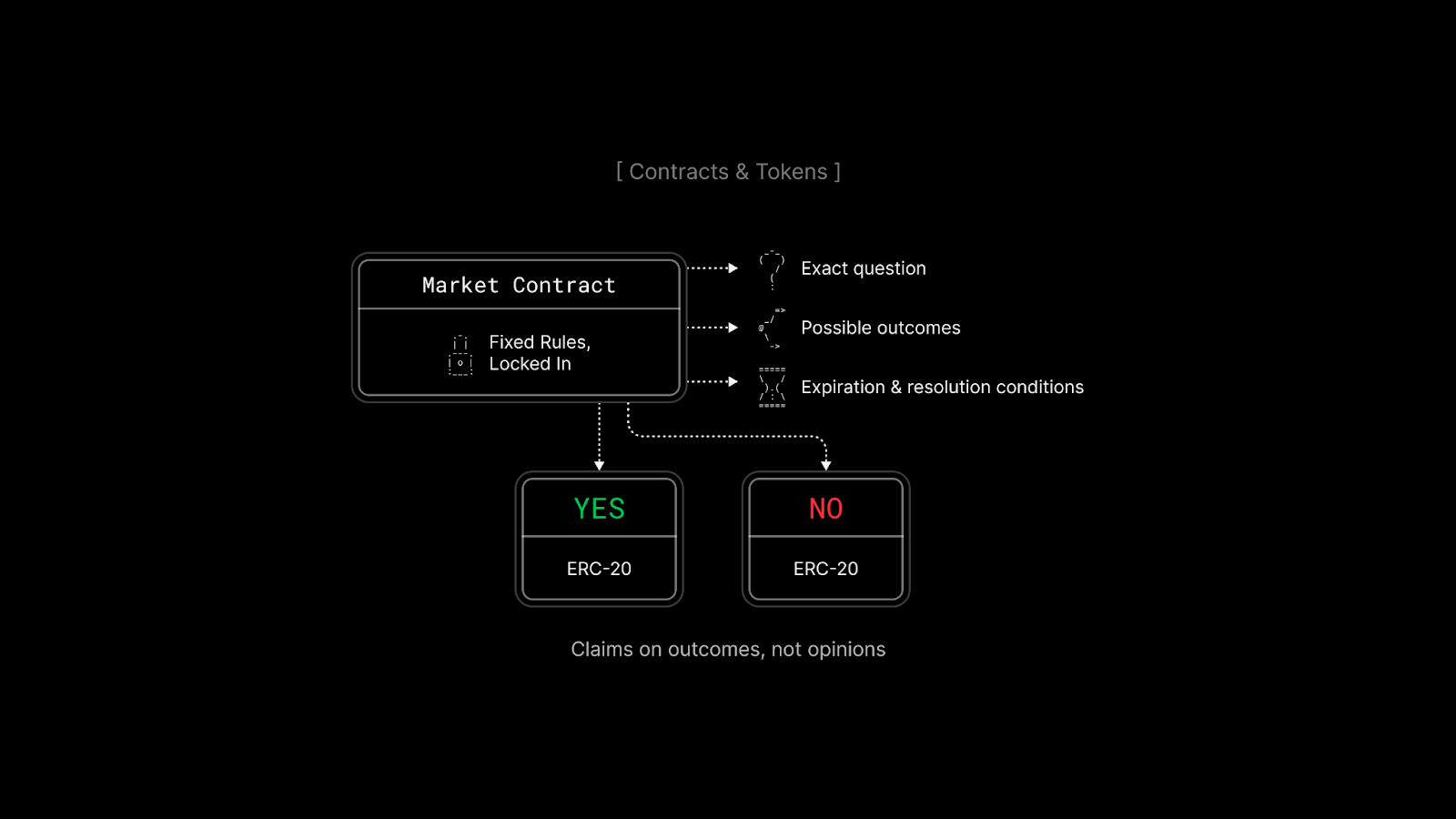
Each possible outcome is represented by its own token, most commonly YES and NO. These tokens behave like standard ERC-20 assets. They can be traded, held, or transferred. Their value depends entirely on what eventually happens. They are not predictions. They are claims on a future state of the world.
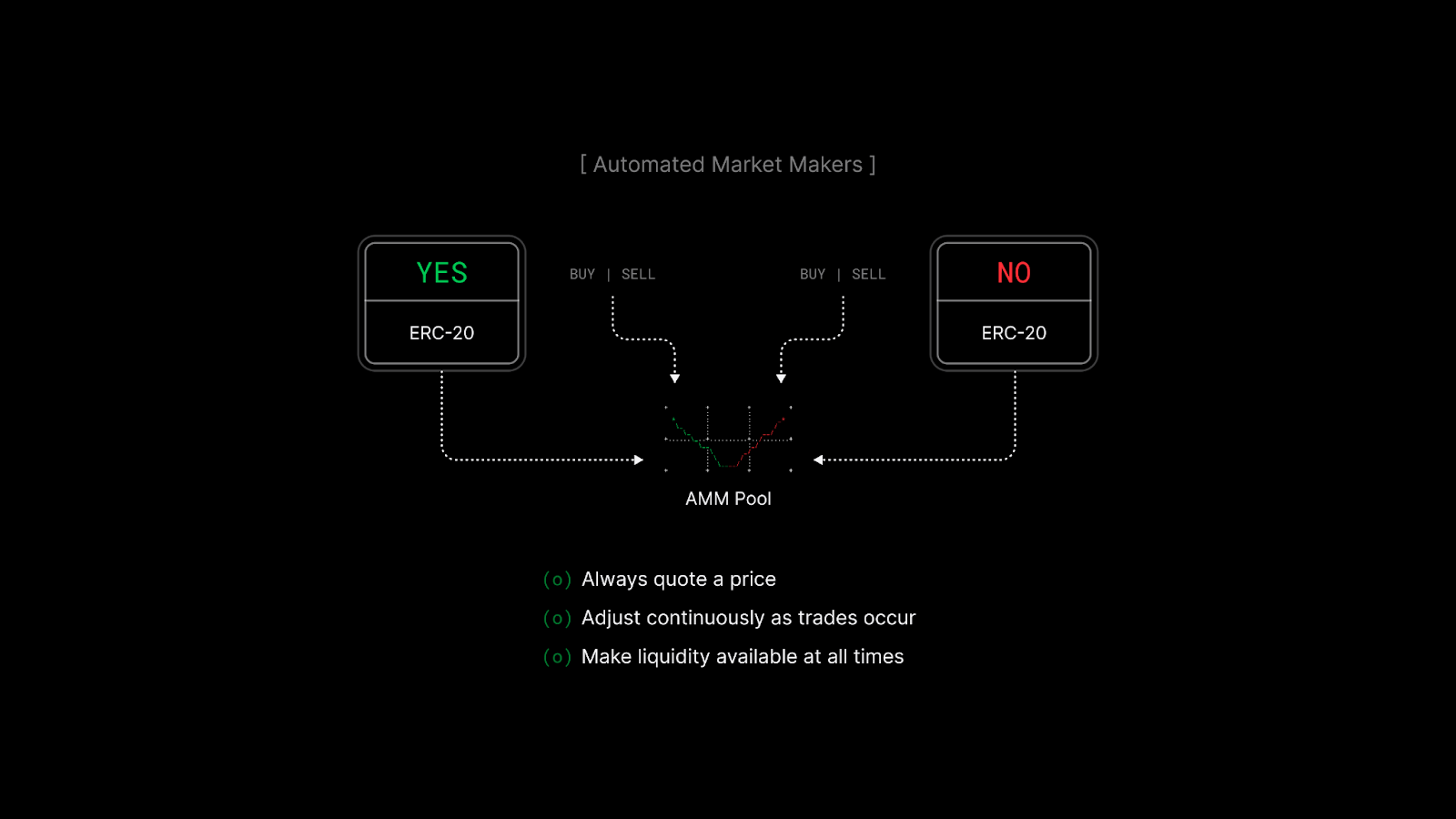
Pricing via AMMs
Rather than depending on order books, most modern markets use Automated Market Makers. Their design keeps markets active and expressive, even when participation is uneven.
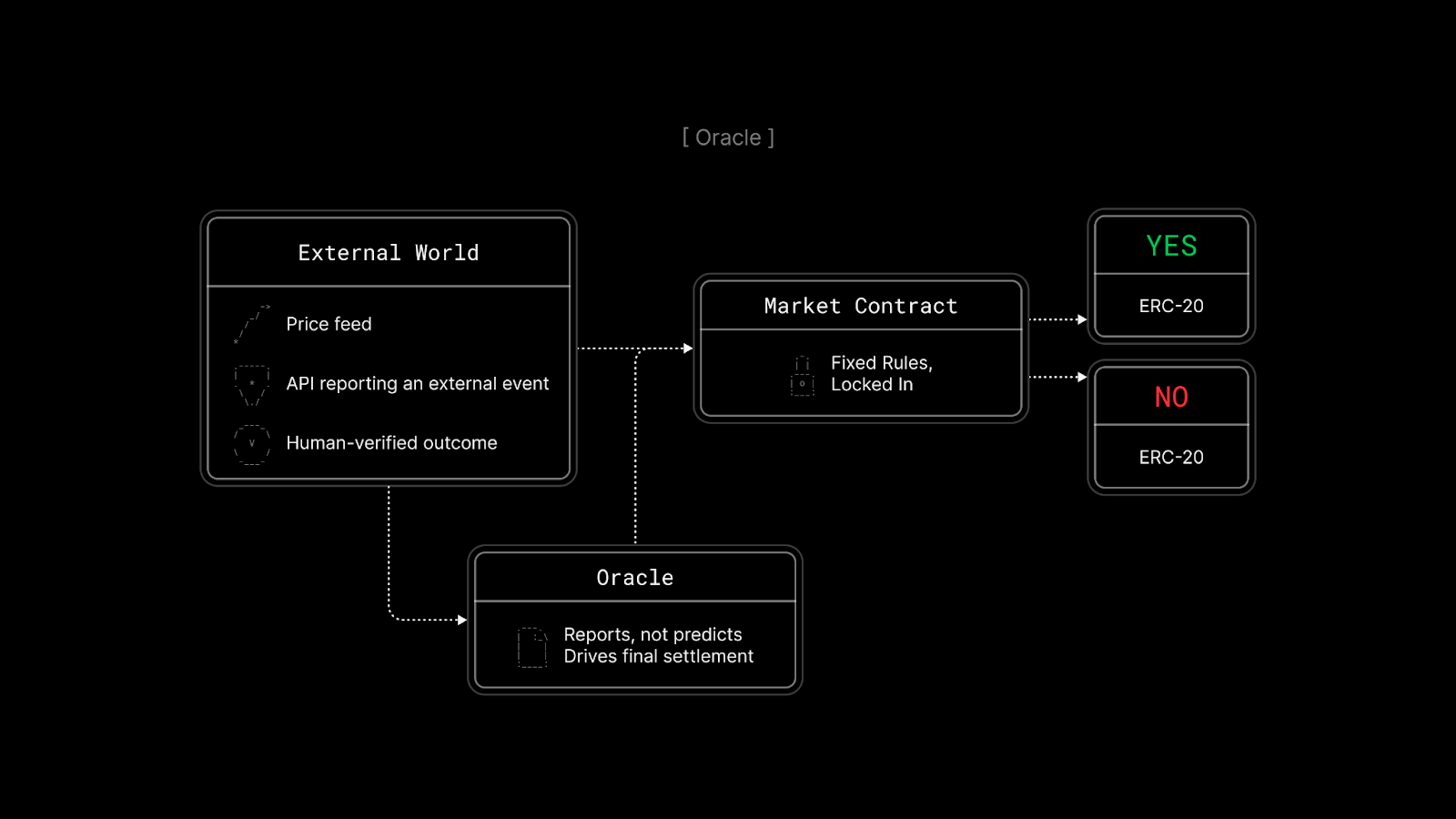
Oracles
At resolution, the market needs an answer. That role belongs to the oracle. Oracles don’t predict anything. They exist solely to report what already happened so the system can settle.
Deterministic Settlement
When the event date arrives, uncertainty collapses into fact. The resolution process is deliberately mechanical.
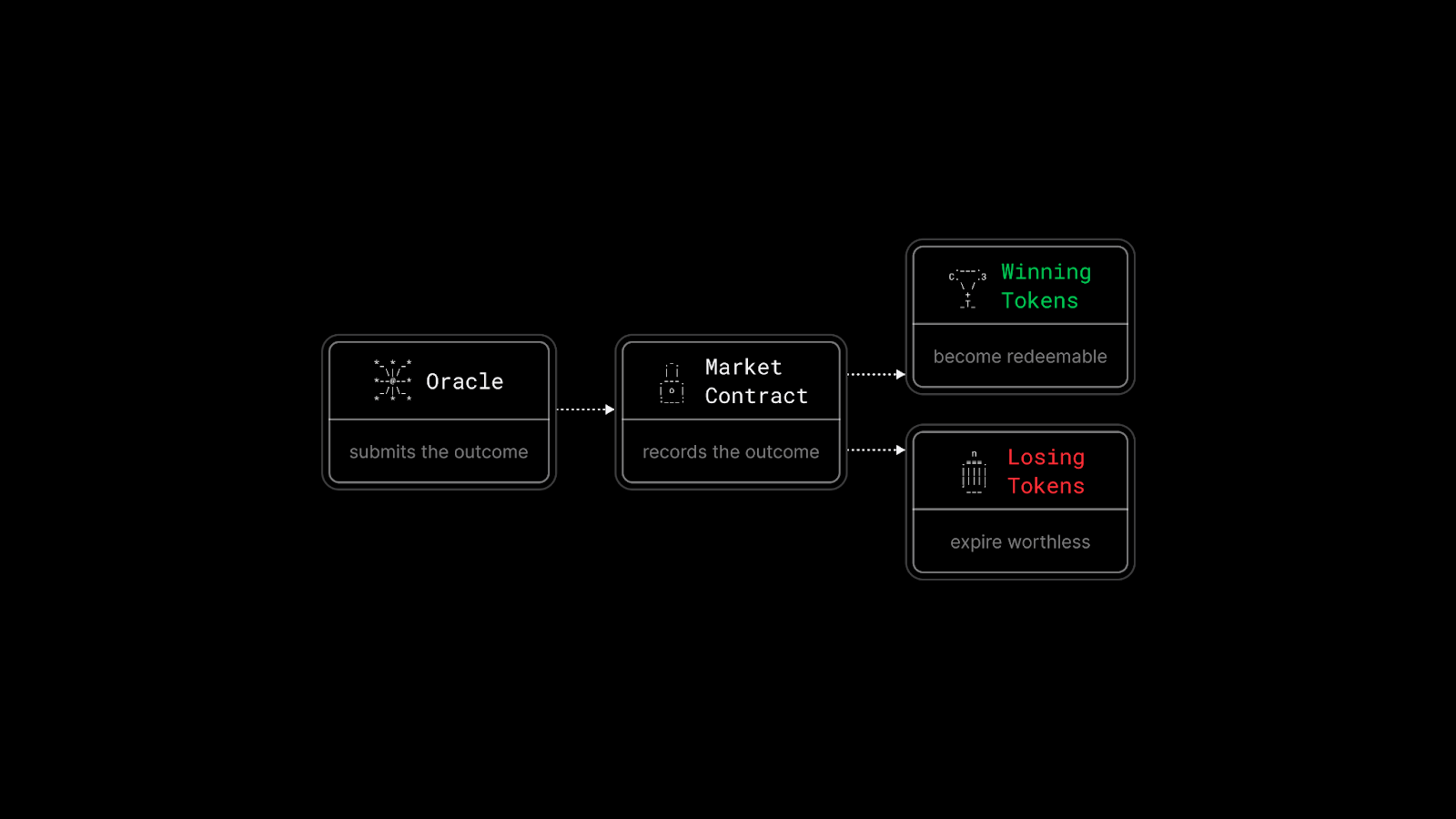
There is no interpretation at this stage. The rules written at the beginning are applied exactly as specified. Resolution is predictable, final, and dull. Trust in prediction markets comes not from clever resolution, but from boring consistency.
Together, these components form a one-way pipeline: belief flows in through trading, and resolution flows out through settlement.
Production-Grade Experiments
These ideas are not theoretical. Several projects shaped how on-chain prediction markets evolved. Through these systems, pricing mechanisms, oracle designs, and settlement rules were tested under real conditions and refined through use.
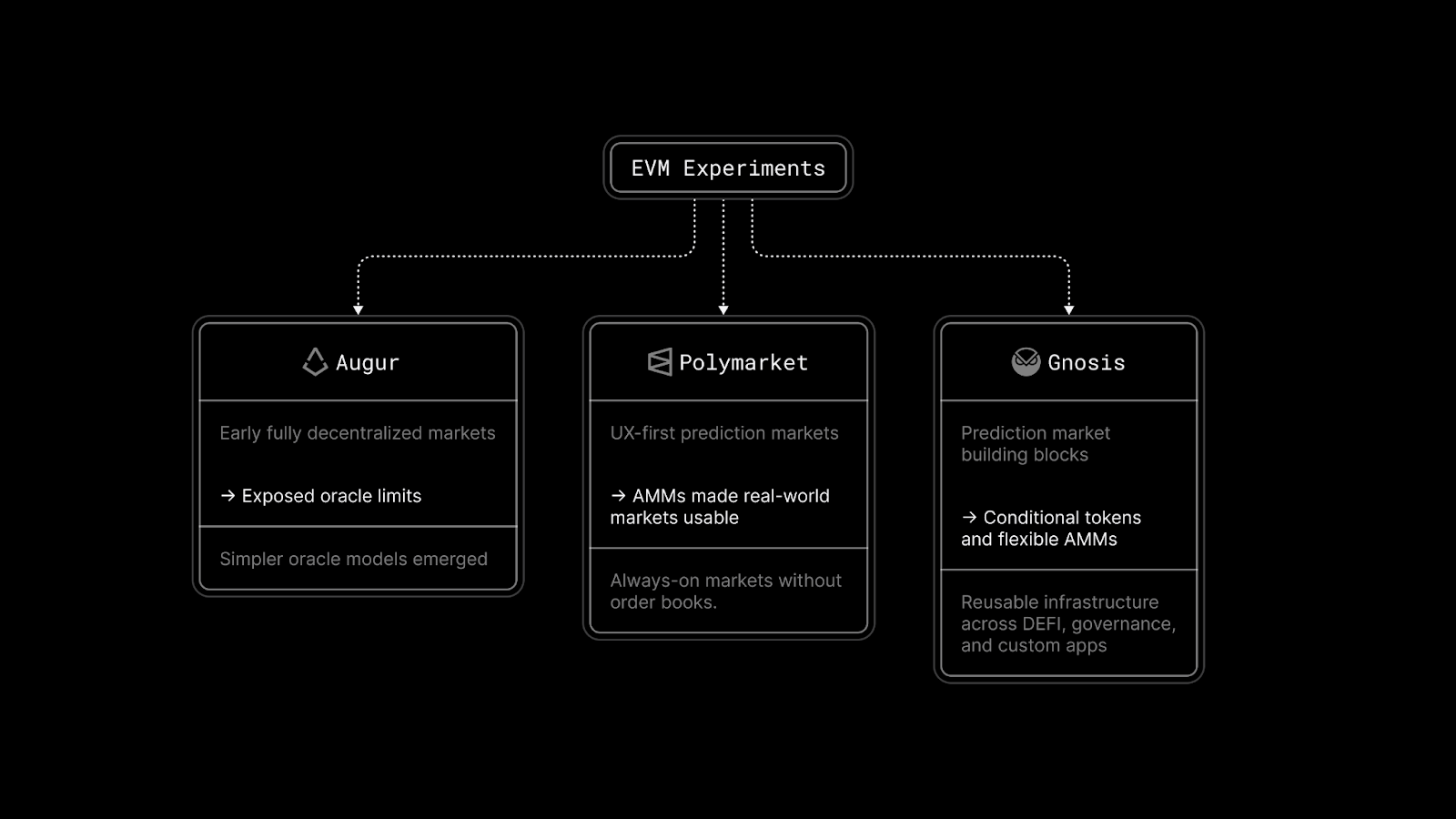
Most of this experimentation has taken place on Ethereum and EVM-compatible networks. These environments made it possible to combine prediction markets with DeFi, governance, and other on-chain systems, accelerating both experimentation and adoption.
Observation Without Action
By moving on-chain, prediction markets solved major problems of trust, access, and integration. They became credible infrastructure rather than fragile platforms. But one limitation remained.
Even on-chain, prediction markets are still observers. They measure belief, refine probabilities, publish signals, and then … they wait. They don’t react to belief as it forms. They don’t trigger behavior elsewhere. They remain informational, even when their signals become sharp and meaningful.
That passivity is not a failure of design. It is simply where the architecture stops. And it is exactly where the next layer begins.
About Reactive Network
Reactive is an EVM-compatible execution layer for dApps built with Reactive contracts. These contracts differ from traditional smart contracts by using inversion-of-control for the transaction lifecycle, triggered by data flows across blockchains rather than by direct user input.
Reactive contracts listen for event logs from multiple chains and execute Solidity logic in response. They can determine autonomously when to transmit data to destination chains, enabling conditional cross-chain state changes. The network delivers fast and cost-effective computation via a proprietary parallelized EVM implementation.
Website | Blog | Twitter | Telegram | Discord | Reactive Docs
Build once — react everywhere!





